단순 연결리스트(simply linked list)로 큐를 구현해보자.
스택과 마찬가지로 큐도 연결리스트로 구현 가능하다. 단순 연결리스트에 2개의 포인터를 추가한 것과 같은데, front로 삭제하고 rear로 삽입한다. FIFO이기 때문에 먼저 들어온 요소가 먼저 삭제된다.
나머지는 [C]스택과 연결리스트에 정의되어 있는 함수들과 같고, 삽입은 enqueue 삭제는 dequeue가 해준다.
마찬가지로 전역변수를 쓸 때와 쓰지 않을 때로 나누어보았다.
(1) 전역변수 사용
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
|
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ERROR_VALUE -300000
typedef struct LinkedNode {
int data;
struct LinkedNode* link;
}Node;
Node* front;
Node* rear;
void init() { front = rear = NULL; }
int is_empty() { return (front == NULL && rear == NULL); }
int size() {
Node* p;
int count = 0;
for (p = front; p != rear; p = p->link) //front에서 rear가 아닐 때가지 돈다
count++;
return count + 1; //위에보면 조건식이 p!=rear일 때까지이니까 rear일 때도 고려해줘야 함!
}
void enqueue(int value) {
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->data = value;
n->link = NULL;
if (is_empty()) front = rear = n;
else {
rear->link = n;
rear = n;
}
}
int dequeue() {
Node* removed = front;
int value;
/*
두 가지의 경우의 수가 있다.
1. 스택 안의 노드 개수가 하나인 경우, 즉 이때 삭제 연산을 하면 front와 rear 둘 다 NULL을 가리켜야 한다.
2. 스택 안의 노드 개수가 2개 이상인 경우
*/
if (is_empty()) {
printf("Queue Empty Error!\n");
return ERROR_VALUE;
}
else if (size() == 1) {
front = rear = NULL;
}
else {
front = removed->link;
value = removed->data;
free(removed);
return value;
}
}
int peek() {
int value;
if (is_empty()) {
printf("Queue Empty Error!\n");
return ERROR_VALUE;
}
else {
value = front->data;
return value;
}
}
void print_all() {
Node* p;
printf("QUEUE STATUS: size=%d\n", size());
for (p = front; p != NULL; p = p->link)
printf("[%2d]->", p->data);
printf("NULL\n");
/*
아니면 for문부터 이렇게 해도 됨
for (p=front; p!=rear; p=p->link)
printf("[%2d]", p->data);
printf("[%2d]\n", p->data);
이러면 마지막꺼 출력해야되니까 한 번 더 넣어줘야 됨!
*/
}
int main(void) {
int value, sel;
init();
while (1) {
do {
printf("1.ENQUEUE 2.DEQUEUE 3.PEEK 4.STATUS 0.EXIT :");
scanf("%d", &sel);
} while (sel < 0 || sel > 4);
if (sel == 1) {
printf("Enter value to enqueue from rear : ");
scanf("%d", &value);
enqueue(value);
}
else if (sel == 2) {
value = dequeue();
if (value != ERROR_VALUE)
printf("[%2d] has been dequeued from front\n", value);
}
else if (sel == 3) {
value = peek();
if (value != ERROR_VALUE)
printf("[%2d] is the front value of QUEUE\n", value);
}
else if (sel == 4) {
if (is_empty()) printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
else print_all();
}
else break;
}
printf("\nE N D O F P R O G R A M");
return 0;
}
|
cs |
++ 이 코드에는 함정이 있다. 오류는 아니지만 돌려보면 dequeue함수에 뭔가 이상한 점이 있다. 밑에 코드와 비교하면 쉽게 찾을 수 있다. 이 때까지만 해도 문제가 있는 걸 몰랐는데, dequeue가 모든 값을 반환하지 않는다는 걸 알았어야 했다...
(2) 전역변수 미사용
전역변수가 예전과 다르게 front, rear 2개이다. 둘 다 main으로 집어넣고 일일이 매개변수로 넘겨야 하나?라고 두려움에 떨고 있었는데, 교재가 멋진 해답을 알려줌. 바로 front와 rear 둘 다 새로운 구조체에 포함시켜버리는 것이다!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ERROR_VALUE -300000
typedef struct LinkedNode {
int data;
struct LinkedNode* link;
}Node;
typedef struct {
Node* front, * rear;
}LinkedType;
void init(LinkedType* q) {
q->front = q->rear = 0;
}
int is_empty(LinkedType* q) {
return (q->front == NULL && q->rear == NULL);
}
int size(LinkedType* q) {
Node* p;
int count = 0;
for (p = q->front; p != q->rear; p = p->link)
count++;
return count + 1;
}
void enqueue(LinkedType* q, int value) {
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->data = value;
n->link = NULL;
if (is_empty(q)) q->front = q->rear = n;
else {
q->rear->link = n; //장난하냐... 순서 헷갈리지 말자
q->rear = n;
}
}
int dequeue(LinkedType* q) {
Node* removed = q->front;
int value;
if (is_empty(q)) {
printf("Queue Empty Error!\n");
return ERROR_VALUE;
}
else if (size(q) == 1) {
value = q->rear->data;
q->front = q->rear = NULL;
return value;
}
else {
q->front = removed->link;
value = removed->data;
free(removed);
return value;
}
}
int peek(LinkedType* q) {
int value;
if (is_empty(q)) {
printf("Queue Empty Error!\n");
return ERROR_VALUE;
}
else {
value = q->front->data;
return value;
}
}
void print_all(LinkedType* q) {
Node* p;
printf("QUEUE STATUS: size=%d\n", size(q));
for (p = q->front; p != NULL; p = p->link)
printf("[%2d]->", p->data);
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main(void) {
LinkedType queue;
int value, sel;
init(&queue);
while (1) {
do {
printf("1.ENQUEUE 2.DEQUEUE 3.PEEK 4.STATUS 0.EXIT :");
scanf("%d", &sel);
} while (sel < 0 || sel > 4);
if (sel == 1) {
printf("Enter value to enqueue from rear : ");
scanf("%d", &value);
enqueue(&queue, value);
}
else if (sel == 2) {
value = dequeue(&queue);
if (value != ERROR_VALUE)
printf("[%2d] has been dequeued from front\n", value);
}
else if (sel == 3) {
value = peek(&queue);
if (value != ERROR_VALUE)
printf("[%2d] is the front value of QUEUE\n", value);
}
else if (sel == 4) {
if (is_empty(&queue)) printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
else print_all(&queue);
}
else break;
}
printf("\nE N D O F P R O G R A M");
return 0;
}
|
cs |
책이 init()함수를 어떻게 구성하면 될지 힌트를 좀 줬다. 대신 main에서 변수를 선언할 때 구조체 포인터를 쓰지 않는다.
내 짧은 경험으로는 이런 적이 처음이다;;; 구조체 쓰려면 항상 포인터 써줘야 하는거 아니였나?
<결과 창>
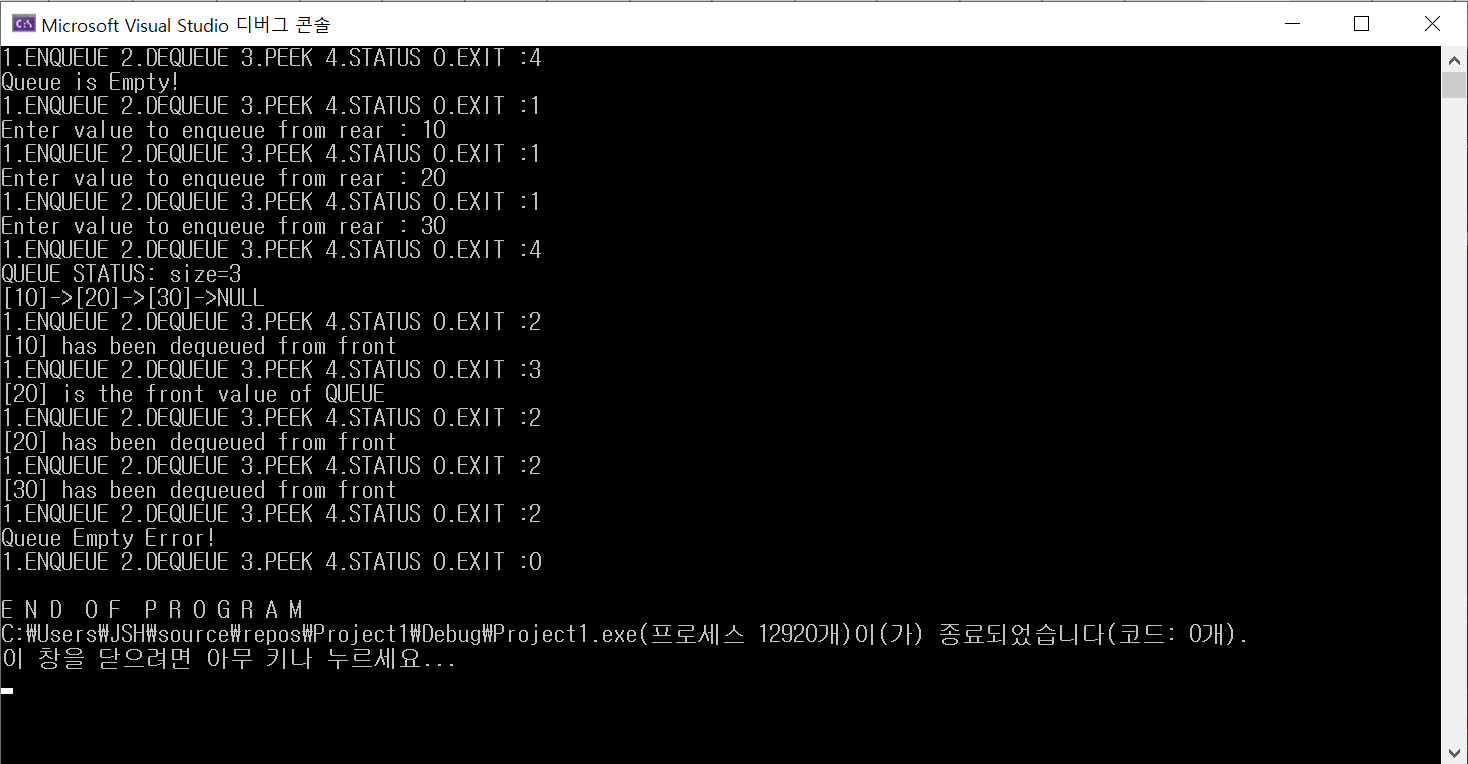
'coding > Data Structure(C)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C] 이진트리의 순회 (0) | 2020.12.12 |
|---|---|
| [C] 트리와 이진트리 (0) | 2020.12.12 |
| [C] 스택과 연결리스트 (0) | 2020.12.12 |
| [C] 리스트와 연결리스트(2) (0) | 2020.12.11 |
| [C] 리스트와 연결리스트(1) (0) | 2020.12.11 |



